-medium.webp)
Table of Contents
This article provides a legal insight into process of the company registration in Nepal and offers a clear roadmap for businesses starting in Nepal.
Company Act 2063 has stated about Four types of company. They are:-
- Public Company
- Private Company
- Profit Not Distributing Company
- Foreign Company
Steps of Company Registration in Nepal
1. Reservation of company name at the company registration office.
The first step of company registration in Nepal is the reservation of the company’s name in the online portal of OCR. The company’s name should not clash with any other registered companies. After the name approval, we can initiate the further process of company registration.
2. Submission of documents
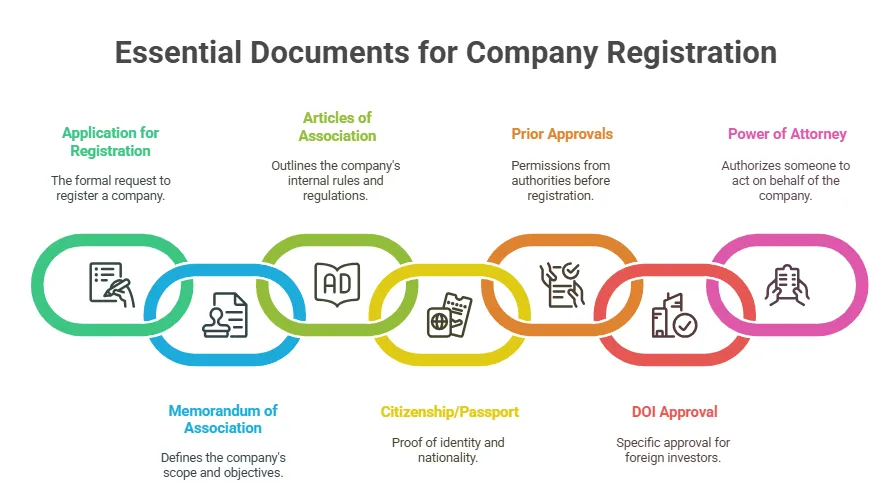
These documents are essential for completing the company registration in Nepal via OCR’s official platform.
1. Application
2. MOA (Memorandum of Association)
3. AOA (Articles of Association)
4. Citizenship / NID in case of Nepali and Passport in case of Foreigner.
5. Prior approval or license from relevant authority (If required)
6. Copy of approval of DOI (In case of a foreign investor)
7. Power of attorney.
3. Authentication by the company registrar's office.
The OCR will review the submitted materials. The staff must either submit more documents or make the necessary revisions if there is a discrepancy in the details or if there are no documents.
4. Payment of registration fee.
Following the review and validation of the proposed company's documentation, the staff is required to pay the government-mandated fees according to the authorized capital. The amount of the government fee is determined by a company's authorized capital. Private and public companies in Nepal pay different company registration fees.
Private company registration fee
The cost structure for company registration in Nepal varies depending on the type of company and authorized capital.
| Amount of Authorized Capital | Government Fee |
|---|---|
| Upto 1,00,000 | 1,000 |
| 1,00,001 to 5,00,000 | 4,500 |
| 5,00,001 to 25,00,000 | 9,500 |
| 25,00,001 to 1,00,00,000 | 16,000 |
| 1,00,00,001 to 2,00,00,000 | 19,000 |
| 2,00,00,001 to 3,00,00,000 | 22,000 |
| 3,00,00,001 to 4,00,00,000 | 25,000 |
| 4,00,00,001 to 5,00,00,000 | 28,000 |
| 5,00,00,001 to 6,00,00,000 | 31,000 |
| 6,00,00,001 to 7,00,00,000 | 34,000 |
| 7,00,00,001 to 8,00,00,000 | 37,000 |
| 8,00,00,001 to 9,00,00,000 | 40,000 |
| 9,00,00,001 to 10,00,00,000 | 43,000 |
| Above 10,00,00,000 | 30 for each 1,00,00,000 |
Public Company Registration Fee
| Amount of Authorized Capital | Government Fee |
|---|---|
| Upto 1,00,00,000 | 15,000 |
| 1,00,00,000 to 10,00,00,000 | 40,000 |
| 10,00,00,000 to 20,00,00,000 | 70,000 |
| 20,00,00,000 to 30,00,00,000 | 1,00,000 |
| 30,00,00,000 to 40,00,00,000 | 1,30,000 |
| 40,00,00,000 to 50,00,00,000 | 1,60,000 |
| More than 50,00,00,000 | 1 crore per 3,000 |
5. Issuance of Company registration certificate.
A company registration certificate will be issued by OCR upon the submission and verification of the necessary paperwork and the payment of the government fees for company registration.
6. Tax registration at the Inland Revenue Office
A PAN number must be obtained after obtaining a certificate attesting to the company's registration. The Permanent Account Number, or PAN for short, is the official method of paying taxes and VAT at the Inland Revenue Department.
Company Compliance is the next step after registration of a company in the office of the company registrar.
The term "company compliance" describes how closely a company operates by the applicable laws, rules, and industry standards. It entails making sure that a business's policies, processes, and procedures comply with these standards in order to reduce the risk of non-compliance and the repercussions that come with it.
After the registration of the company, it has to comply with the post-registration process. They are: -
- Registration of business at the local level.
- Obtaining a PAN certificate from the Inland Revenue Office.
- Opening a Bank Account.
- Additional approval or licenses for the business (If required)
Registration of Business at Local Level
Business registration at the sub-national level in Nepal is normally done at the ward level by obtaining a "Ward Registration" or "Local Municipality Registration" from the concerned municipal or rural ward office. An application form with all documents, such as the citizenship certificate of the owner, passport-sized photos, proof of address, and business details like name and type, should be submitted for it. It may also require a business blueprint or recommendation letter from the municipality. A nominal fee may be charged according to the business type and size. Upon approval, the municipality issues a certificate, allowing the business to legally operate within its jurisdiction and abide by local regulations. After being registered in OCR, the company is to be registered in respective Local level.
The documents required for registration at the local level are as follows:-
- Application
- Company Registration Certificate
- Citizenship of all shareholders
- MOA (Memorandum of Association)
- AOA (Articles of Association)
- Rental contract
- Tax clearance receipt of the rented house.
- Minute
Registration of PAN at Inland Revenue Office.
To be registered for a PAN, one has to visit the nearest IRO. Fill out the PAN registration form prescribe by the portal of IRO, with proper details: name, address, type of business, and financial information. Documents required: a citizenship certificate for individuals, a company registration certificate, a business operation certificate for businesses, and recent passport-sized photographs. Submit the form along with the aforementioned documents to the IRO. After verification, the office issues a unique PAN, essential for tax compliance. PAN registration is mandatory for businesses and individuals engaged in taxable activities, enabling smooth financial transactions and tax record management in Nepal. The Inland Revenue Department (IRD) regulates the registration procedure for Permanent Account Numbers (PANs) in Nepal through specific statutes. The Nepal Income Tax Act of 2002 (2058) establishes the legal framework for mandatory PAN possession.
After being registered at OCR and the ward office, the next stop for registration is the Inland Revenue Office. The documents required for registration at the Inland Revenue Office are as follows:-
- Application
- MOA (Memorandum of Association)
- AOA (Articles of Association)
- Company registration certificate by company registrar
- Registration certificate by Ward
- Rental contract
- Land ownership document
- Documents sent by company registrar.
- Minute
- Citizenship of all shareholders
First compliance
A company shall send the following information to the OCR within 3 months after being registered. The company shall provide the prescribed information in a prescribed format as per law:-
- Registered address of company.
- Appointment of Auditor for the fiscal year.
- Share registry
- Director’s Declaration
Annual compliance
A company shall conduct an AGM (Annual General Meeting) within a year of it’s incorporation date. Yearly submission of the report of AGM is to the OCR in order to update the company. The company shall provide the following information to the OCR.
- AGM minutes at OCR.
- Audit Report at OCR.
- Appointment of auditor for next fiscal Year.
The steps, therefore, for company registration in Nepal are well-set: name reservation, submission of documents, payment of a registration fee, the issuance of a registration certificate, and then tax registration. For the operation to be smooth without any penalties, the requirements set by the Company Act 2063 and other legal frameworks have to be met. The companies are required to satisfy certain post-incorporation formalities, such as registration at the sub-national level, getting a PAN, and ensuring annual compliance. Such procedures not only establish an enterprise as a legal entity but also contribute to gaining stakeholders' confidence through transparency and accountability in the affairs of the company.
Frequently Asked Questions
The process begins with the reservation of the company name through the OCR (Office of Company Registrar) online portal. It ensures that the proposed name does not conflict with any existing registered company.
The registration fee is based on the company’s authorized capital and varies between private and public companies. The OCR has set a tiered structure for both categories, with the amount increasing based on the capital declared.
Once the submitted documents are verified and the registration fee is paid, the Office of the Company Registrar issues the company registration certificate. This certificate formally recognizes the company as a legal entity.
Yes. After company registration, it is compulsory to register for a Permanent Account Number (PAN) at the Inland Revenue Office. PAN is essential for tax filing, VAT registration, and other statutory compliance.
Newly registered companies must ensure local registration at the municipal ward office, open a business bank account, obtain required licenses, and file prescribed details like registered address, auditor appointment, and shareholder records within 3 months.
All companies must hold an Annual General Meeting (AGM) and submit the audit report, AGM minutes, and auditor appointment for the next fiscal year to the OCR annually. Failure to do so may lead to penalties or deregistration.
Yes, foreign nationals or companies can register a business in Nepal, provided they fulfill the DOI (Department of Industry) clearance, submit a valid passport, and comply with foreign investment regulations under Nepalese law.
Failure to comply with registration or post-registration obligations—such as failing to register at the ward level, obtain a PAN, or submit annual filings—may result in legal penalties, operational restrictions, or cancellation of registration.
Disclaimer:
This article is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be interpreted as legal advice, advertisement, solicitation, or personal communication from the firm or its members. Neither the firm nor its members assume any responsibility for actions taken based on the information contained herein.


